Autism Spectrum Disorder
Unlike traditional psychiatry, which rarely looks at the brain, Amen Clinics uses brain imaging technology to identify brain patterns associated with autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is characterized by deficiencies in social and communication skills, limited and repetitive behaviors and interests, and in many (but not all) cases, developmental disabilities including intellectual and language impairments. These symptoms can range from mild to severe. For example, what used to be known as Asperger’s disorder would be on the mild end of the spectrum and what was called classic autism—the most serious form of the condition—would be on the opposite end of autism spectrum disorders.
Who has Autism Spectrum Disorder?
The prevalence of ASD has been increasing at an alarming rate in the past few decades. According to the CDC (Centers for Disease Control), just 10 years ago 1 in 69 children received an autism spectrum disorder diagnosis, and today, an estimated 1 in 44 children are currently affected by the condition. Boys are 4 times more likely than girls to be diagnosed with ASD.
What are the Core Symptoms of ASD?
The signs of autism spectrum disorder typically appear by age 2 or 3 of a child’s life, but if developmental delays are more severe, autism symptoms may become evident in very young children, including those under age 1. ASD affects each person differently. The following list includes several of the core symptoms of autism; however, because it is a spectrum disorder, not all people with an ASD diagnosis will have every symptom.
- Deficits in non-verbal communication, such as understanding social cues and reading facial expressions
- Difficulty with reciprocal communication or ability to initiate communication with other children or adults
- Repetitive movements, such as rocking or hand flapping
- Rigid adherence to routines and habits
- Repetitive use of objects, such as always lining up toys or turning things upside down
- Behavioral symptoms
- Difficulty learning new skills
- Aversion to change
- Sensory sensitivities
- Having an intense focus on certain things
- Echolalia (repeating words or sentences others say)
- Speech delays or significantly impaired language skills
- Poor eye contact
- Deficits with social skills
- Sleep disorders
- Narrow food preferences
- Intellectual disability
- Self-injurious behavior, such as repetitive head-banging, scratching, or biting
- Social isolation, particularly for older people with autism spectrum disorder who live alone

When children with autism spectrum disorder are untreated, misdiagnosed, or have a delayed diagnosis of autism (ASD), it is associated with higher incidences of other medical conditions and mental disorders, including:
- Other developmental disabilities and related problems
- More severe symptoms
- Immune disorders (allergies, asthma)
- Diabetes
- Heart disease
- Motor disorders
- Cancer
- Obesity
- Schizophrenia
- Suicidal thoughts and behavior
What Causes Autism Spectrum Disorder?
It is now known that ASD does not have a singular cause. Research suggests that this is a developmental disability caused by a genetic component that can be influenced by environmental factors to trigger the condition. Certain circumstances that increase the risk for being on the autism spectrum have also been identified, including having older parents, having a sibling with ASD, very premature birth or really low birth weight, fetal exposure to the medication valproate, and maternal pregnancies less than one year apart.
Untreated, misdiagnosed, or delayed diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder is associated with an increased risk for:
- Worsening of symptoms and developmental problems
- Immune disorders (allergies, asthma)
- Diabetes
- Heart disease
- Cerebral palsy and related motor disorders
- Cancer
- Obesity
Why Choose Amen Clinics for ASD Diagnosis and Treatment?
In addition to understanding an ASD patient’s brain pattern, the use of SPECT imaging at Amen Clinics provides additional benefits. Adults and children with autism spectrum disorder often struggle with other mental health conditions, such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), depression, and anxiety as well as medical issues like epilepsy, gastrointestinal problems, and sleep disturbances. According to a growing body of research, over 70% of children with autism spectrum disorder have other co-existing medical conditions or psychiatric disorders, and more than 40% have two or more such conditions. SPECT imaging can reveal the presence of other brain problems so that a targeted autism treatment plan can be developed to address all the issues affecting you or your child. The sooner a child with this condition receives autism spectrum disorder treatment, the more effective it will be. Early diagnosis and intervention can help with a child’s development overall and decrease symptoms as your child grows up. It’s important to know that adults with ASD can benefit from autism treatment options too.
Autism Brains Work Differently
Autism spectrum disorder is one of the fastest growing developmental disorders in the U.S. today. Early brain development is affected by ASD, including the way neurons communicate with one another leading to a wide array of problems including difficulty with everyday skills. However, there is not just one brain problem found in adults and children with autism—there are 8 to 10 suspected factors that can influence abnormal brain function leading to this developmental disability. During the past three decades, Amen Clinics has seen more than 1,000 children and adults with an autism diagnosis. The SPECT imaging studies of these patients reveal that their brain patterns tend to have areas of high activity, low activity, or areas of both in some cases. Knowing a patient’s brain pattern can lead to more effective treatment options.
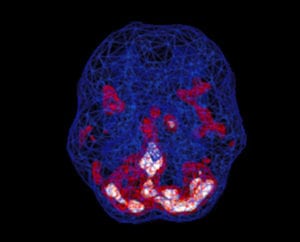
Healthy Brain Scan
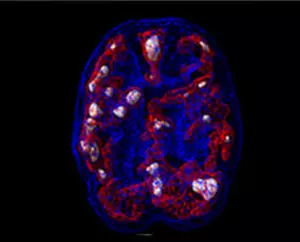
ASD Brain Scan
Because brain patterns in autism spectrum disorder can be varied, it is even more important to look at the brain using SPECT imaging in order to create the most effective autism treatment plan. Abnormal activity is often seen in the cerebellum, anterior cingulate gyrus, amygdala, and the temporal, frontal, and parietal lobes. Brain SPECT scans also serve as a very useful tool for measuring the progress of treatment and positive changes in an adult’s or child’s symptoms and to continue finding the best and most effective treatment options for each patient. These range widely and might include teaching children (or adults) behavior modifications to reduce unwanted behaviors, techniques to improve social communication and social interactions, educational interventions, life skills training, speech therapy, medication and/or supplement management, sensory integration therapy, lifestyle adjustments, and physical therapy as well as complementary and alternative treatments.
SPECT (single photon emission computed tomography) is a nuclear medicine study that evaluates activity (blood flow) in the brain. Basically, it shows three things: healthy activity, too little activity, or too much activity. In an “active” scan, blue represents average blood flow, while red and white represent increasingly higher levels of blood flow. In the healthy scan on the left, the most active area is the cerebellum, located in the back/bottom part of the brain, which is normal. The scan on the right of a 9-year-old boy with ASD reveals abnormally high activity in many areas of the brain, as well as low activity in the cerebellum.
Ready to learn more? Speak to a care coordinator today!
Contact UsHigh & Low Activity Patterns in Autism Spectrum Disorder
In settings outside of Amen Clinics, the diagnosis of ASD is usually determined by a clinical history, criteria from the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM) published by the American Psychiatric Association, the autism mental status examination, and other structured screening tools, leaving clinicians in the dark about the underlying brain function problems. With brain SPECT imaging, an adult or child psychiatrist will frequently see increased activity in the anterior cingulate gyrus—linked to rigid, obsessive behavior—along with decreased activity in the temporal lobes (associated with language and deficits in social interactions), and in the cerebellum, which is involved with learning and physical coordination.
High Activity Patterns in ASD
Increased activity in the anterior cingulate gyrus and lateral prefrontal cortex, linked to symptoms such as:
- Repetitious speech and behavior
- Getting stuck on thoughts and routines
- An adult’s or child’s ability to cope well with transitions and change
An overall increase of activity throughout the brain, which may be associated with inflammation, and contribute to symptoms of:
- Mood instability
- Emotional meltdowns
- Anxiety
Low Activity Patterns in ASD
A smaller, less active cerebellum, associated with:
- Impeded or poor motor skills
- Problems with learning and thought coordination
Overall decreased activity on the surface of the brain as well as in the parietal and temporal lobes, contributing to:
- Difficulty with communication skills
- Learning deficits
- Problems with social skills
- Sensory processing issues
- Problems with abstract thinking
- Deficits with language skills
“With A Better Brain Comes A Better Life”
– Daniel G. Amen, M.D.


