Depression
Unlike traditional psychiatry, which rarely looks at the brain, Amen Clinics uses brain imaging technology to identify brain patterns associated with the 7 types of depression.
What is Depression?
Depression (known as clinical depression or major depressive disorder) is the most common mental health problem in the nation and across the globe. Everybody gets the blues from time to time. For most of us, we bounce back from these low moods and get back to enjoying our lives. For some people, however, the sense of sadness, emptiness, or hopelessness doesn’t dissipate, and it begins to affect how you think, how you feel, and how you act. When these feelings persist, this mood disorder can interfere with daily life and that can lead to psychological and physical issues.
Who has Depression?
Approximately 17.3 million people in America are affected by depression, representing over 7% of the adult population. The condition is more common in females, who are twice as likely as men to suffer a depressive episode. Research shows the condition is rising most rapidly among teens and young adults. About 36% of girls will experience clinical depression during their teenage years compared to 13% of teenage boys.
Consequences of Untreated Depression?
It is estimated that nearly 2 out of every 3 people struggling with depression don’t seek or receive treatment for their condition. When left untreated, depression can ruin your life. Clinical depression increases the risk of substance abuse, destroys relationships, interferes with your ability to excel at work, and makes you more vulnerable to certain medical conditions. For example, people with depression are more likely to develop heart disease and are more likely to die following a heart attack than people without the condition. Even more troubling is the fact that depression is the cause of two-thirds of suicides.

Untreated depression severely increases the risk of:
- Substance abuse
- Relationship problems
- Work problems
- Heart disease
- Suicide
Why Choose Amen Clinics for Treating Depression?
It is not uncommon for depression to be misdiagnosed for other mood disorder, such as bipolar disorder, or for other conditions like ADD/ADHD or even dementia. Getting the wrong diagnosis and the wrong treatment can make your symptoms worse and keep you in a downward spiral. Our brain imaging work allows us to distinguish depression from other conditions and to identify any co-existing issues that also need to be treated. Brain imaging has taught us that depression is not a single or simple disorder, and that giving everyone who’s depressed the same medication will never work. Based on your brain scans, we can better determine how you will respond to treatment so you can feel better faster.
Depressed Brains Work Differently
Brain imaging studies show that depression is not a character flaw or personal weakness. It is associated with biological changes in the brain. People with depression often have too much activity in the deep limbic system—the brain’s emotional centers. But not everyone with depression has the same underlying brain patterns. Brain imaging has taught us is that there are 7 different brain patterns associated with depression, and knowing your type can be the key to getting the most effective treatment.
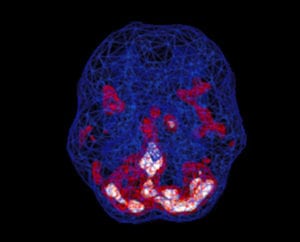
Healthy Brain Scan
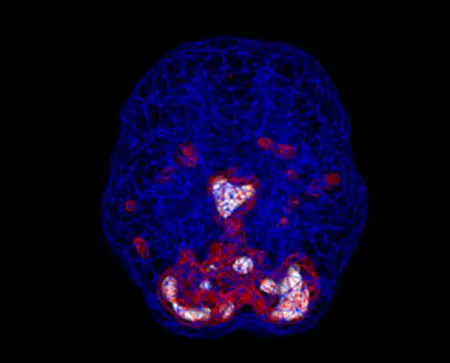
Depressed Brain Scan
SPECT (single photon emission computed tomography) is a nuclear medicine study that evaluates blood flow and activity in the brain. Basically, it shows three things: healthy activity, too little activity, or too much activity. A healthy “active” scan shows the most active parts of the brain with blue representing the average activity and red (or sometimes red and white) representing the most active parts of the brain. In the healthy scan on the left, the most active area is in the cerebellum, at the back/bottom part of the brain. The brain scan on the right shows overactivity in the deep limbic system (the brain’s emotional center), a pattern commonly seen in depression.
Ready to learn more? Speak to a care coordinator today!
Contact Us7 Types of Depression
Our brain imaging work at Amen Clinics has helped us identify 7 different brain patterns associated with depression. And each type requires its own treatment plan.
Type 1: Pure Anxiety
Did you know that depression and anxiety occur together 75% of the time? For this reason, we include anxiety as one of the 7 types of depression. Pure Anxiety often results from too much activity in the basal ganglia, setting one’s “idle speed” on overdrive.
Common symptoms of Pure Anxiety include:
- Frequent feelings of nervousness or anxiety
- Panic attacks
- Avoidance of people or places due to a fear of having anxiety or panic attacks
- Symptoms of heightened muscle tension (headaches, sore muscles, hand tremor)
- Periods of heart pounding, nausea, or dizziness
- Tendency to predict the worst
- Multiple persistent fears or phobias (such as dying or doing something crazy)
- Conflict avoidance
- Excessive fear of being judged or scrutinized by others
- Being easily startled or a tendency to freeze in anxiety-provoking or intense situations
- Shyness, timidity, and getting easily embarrassed
Biting fingernails or picking skin
Type 2: Pure Depression
Pure Depression often results from excessive activity in the deep limbic system—the brain’s emotional center. People with this type struggle with depressive symptoms that range from chronic mild sadness (dysthymia) to crippling major depression, where it’s difficult to even get out of bed.
Common symptoms of Pure Depression include:
- Persistent sad or negative mood
- Loss of interest in usually pleasurable activities
- Restlessness, irritability, or excessive crying
- Feelings of guilt, worthlessness, helplessness, hopelessness, or pessimism
- Sleeping too much or too little, or early-morning awakening
- Appetite changes and/or weight loss or weight gain
Decreased energy or feeling “slowed down” - Thoughts of death or suicide, or suicide attempts
- Difficulty concentrating, remembering, or making decisions
- Persistent physical symptoms (such as headaches, digestive problems, or chronic pain)
- Chronic low self-esteem
- Persistent feeling of being dissatisfied or bored
Type 3: Mixed Anxiety / Depression
Mixed Anxiety/Depression involves a combination of both Pure Anxiety symptoms (listed above) and Pure Depression symptoms (listed above). This type shows excessive activity in the brain’s basal ganglia and the deep limbic system. One type may predominate at any point in time, but symptom of both are present on a regular basis.
Type 4: Over-focused Anxiety / Depression
Over-Focused Anxiety/Depression involves excessive activity in the brain’s anterior cingulate gyrus, basal ganglia, and/or the deep limbic system. People with this type—which occurs more frequently in the children or grandchildren of alcoholics—have trouble shifting attention and often get locked into anxious and/or negative thoughts or behaviors. This can look like:
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder (stuck on negative thoughts or actions)
- Phobias (stuck on a fear)
- Eating disorders (stuck on negative eating behavior)
- Posttraumatic stress disorder or PTSD (stuck on a past traumatic event)
Common symptoms of Over-focused Anxiety/Depression include 4 symptoms from Pure Anxiety (listed above) and/or Pure Depression (listed above), plus at least 4 of the following:
- Excessive or senseless worrying
- Upset when things are out of place or things don’t go the way you planned
- Tendency to be oppositional or argumentative
- Tendency to have repetitive negative or anxious thoughts
- Tendency toward compulsive or addictive behaviors
Intense dislike for change - Tendency to hold grudges
- Difficulty seeing options in situations
- Tendency to hold onto own opinion and not listen to others
- Needing to have things done a certain way or you become upset
- Others complain you worry too much
- Tendency to say “no” without first thinking about the question
Type 5: Temporal Lobe Anxiety / Depression
Temporal Lobe Anxiety/Depression is related to too little or too much activity in the temporal lobes (involved in moods, emotions, and memory), in addition to overactivity in the basal ganglia and/or deep limbic system.
Common symptoms of Temporal Lobe Anxiety/Depression include 4 symptoms from Pure Anxiety (listed above) and/or Pure Depression (listed above), plus at least 4 of the following:
- Short fuse or periods of extreme irritability
- Periods of rage with little provocation
- Often misinterpreting comments as negative when they are not
- Periods of spaciness or confusion
- Periods of panic and/or fear for no specific reason
- Visual or auditory changes, such as seeing shadows or hearing muffled sounds
- Frequent periods of déjà vu
- Sensitivity or mild paranoia
- Headaches or abdominal pain of uncertain origin
- History of head injury
- Family history of violence or explosiveness
- Dark thoughts that may involve suicidal or homicidal thoughts
- Periods of forgetfulness or memory problems
Type 6: Cyclic Anxiety / Depression
Cyclic Anxiety/Depression is associated with extremely high activity in the brain’s basal ganglia and/or deep limbic system. These areas of excessive activity act like “emotional seizures” as the emotional centers hijack the brain for periods of time in a cyclical pattern. Cyclical disorders, such as bipolar disorder, cyclothymia, premenstrual tension syndrome, and panic attacks are part of this category because they are episodic and unpredictable.
Common symptoms of Cyclic Anxiety/Depression include 4 symptoms from Pure Anxiety (listed above) and/or Pure Depression (listed above) plus periods of time with at least 4 of the following:
- Abnormally elevated, depressed or anxious mood
- Decreased need for sleep, feeling energetic on dramatically less sleep than usual
- Grandiose notions, ideas or plans
- Increased talking or pressured speech
- Racing thoughts
- Markedly increased energy
- Poor judgment leading to risk taking behavior (departure from usual behavior)
- Inappropriate social behavior
- Irritability or aggression
- Delusional or psychotic thinking
Type 7: Unfocused Anxiety / Depression
Unfocused Anxiety/Depression is associated with low activity in the prefrontal cortex (PFC) in addition to high activity in the basal ganglia and/or deep limbic system. The PFC is involved with attention, focus, impulse control, judgment, organization, planning, and motivation. When the PFC is underactive, people often have problems with these executive functions.
Distinguishing Unfocused Anxiety/Depression from ADD/ADHD can be difficult because of the similarity in symptoms. However, brain imaging provides a window into the brain to see the areas with too little or too much activity. This allows for a more accurate diagnosis.
Symptoms of Unfocused Anxiety/Depression include at least 4 items from the Pure Anxiety (listed above) and/or Pure Depression symptoms (listed above), plus at least 4 of the following:
- Trouble staying focused
- Spaciness or feeling in a fog
- Overwhelmed by the tasks of daily living
- Feeling tired, sluggish or slow moving
- Procrastination, failure to finish things
- Chronic boredom
- Distractibility
- Forgetfulness
- Difficulty expressing feelings
- Lack of empathy for others
A variation of Unfocused Anxiety/Depression is caused by overall reduced blood flow and activity in the cortex along with too much activity in the basal ganglia and/or deep limbic system. This pattern may be related to physical illness, drug or alcohol abuse, hypoxia (lack of oxygen), infections (such as Lyme disease), traumatic brain injury, or exposure to toxic mold or other environmental toxins. Symptoms of this variation also include frequent feelings of sickness, mental dullness, “brain fog,” or cognitive impairment.
“With A Better Brain Comes A Better Life”
– Daniel G. Amen, M.D.


